Planning for retirement is crucial in ensuring a secure future, and understanding the nuances of tax planning plays a vital role. In this article, we will explore the various strategies and considerations that can help you maximize your savings and minimize your tax liability, thus setting a strong financial foundation for your retirement years.
The Role of Taxes in Retirement Planning
When it comes to planning for retirement, taxes play a crucial role in securing your financial future. Understanding how taxes impact your retirement savings and income is essential for making informed decisions. Here are some key considerations:
Tax-efficient savings strategies
One aspect of retirement planning involves choosing tax-efficient savings strategies. Contributing to retirement accounts such as 401(k)s or IRAs can provide immediate tax benefits. These contributions are often tax-deductible, meaning you can lower your taxable income and potentially reduce your tax liability in the present.
Tax-deferred growth
Another important consideration is the concept of tax-deferred growth. Many retirement accounts allow your investments to grow tax-deferred until you take distributions. This means you can postpone paying taxes on your earnings until you withdraw funds in retirement when you may be in a lower tax bracket.
Withdrawal strategies
Developing a thoughtful withdrawal strategy is crucial for minimizing tax implications during retirement. Different types of retirement accounts have varying tax rules, and withdrawals may be subject to ordinary income tax. By choosing the right accounts to tap into and managing your withdrawals strategically, you can help optimize your retirement income and minimize taxes.
Social Security and tax implications
Many retirees rely on Social Security benefits as a source of income in retirement. However, it’s important to note that depending on your total income, these benefits may become taxable. Understanding the rules and potential tax implications of receiving Social Security is essential to avoid any surprises when tax season arrives.
Healthcare costs and tax planning
Healthcare costs are a significant expense for many retirees. Having a tax-efficient strategy to cover these costs is essential. Understanding the tax benefits of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or deducting qualified medical expenses can help you save money on healthcare-related taxes.
In conclusion, taxes play a crucial role in retirement planning. Being aware of tax-efficient savings strategies, tax-deferred growth opportunities, withdrawal strategies, tax implications of Social Security benefits, and healthcare-related tax planning can help you secure your future and make the most of your retirement savings.
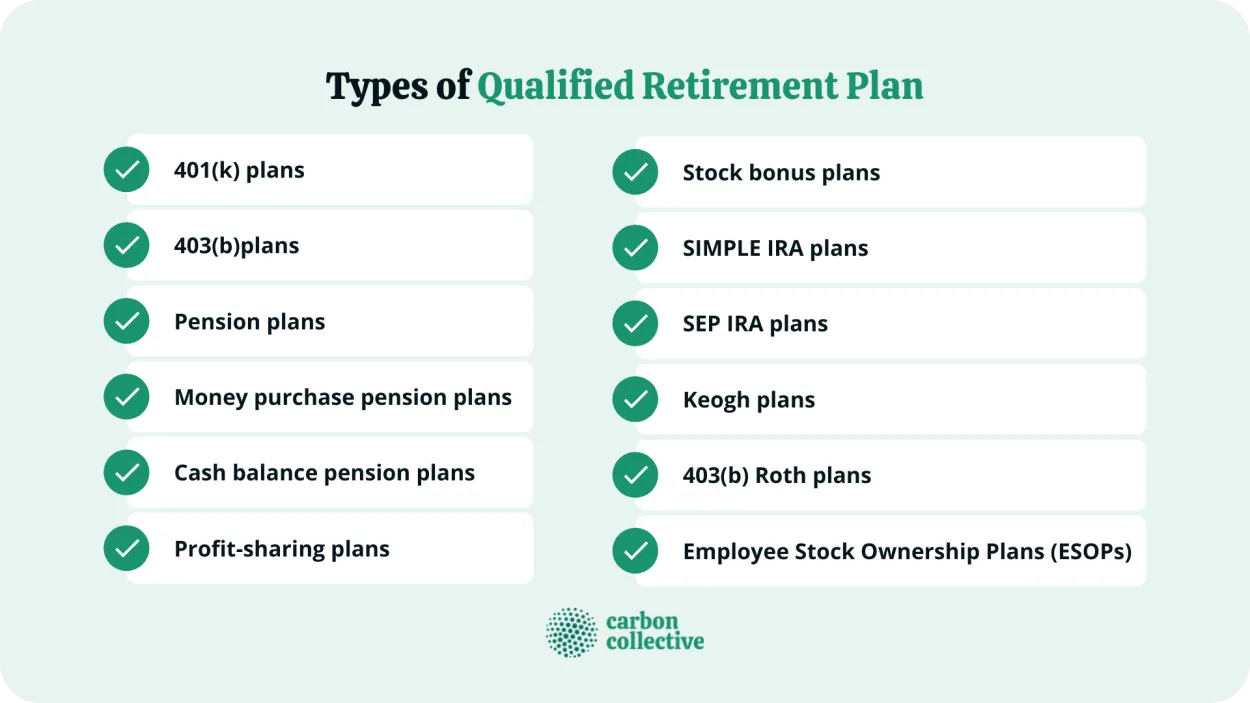
Understanding Tax-Advantaged Retirement Accounts
Tax-advantaged retirement accounts play a vital role in effective tax planning for a secure future. These accounts offer individuals a way to grow their savings over time with various tax advantages. By understanding the different types of tax-advantaged retirement accounts available, you can make informed decisions about your financial future.
1. Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Traditional IRAs allow individuals to contribute pre-tax dollars, meaning that contributions are made with money that has not been subject to income tax. The contributions and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement when they are subject to income tax.
2. Roth Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Roth IRAs differ from traditional IRAs in that contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning that income tax has already been paid. However, the earnings and withdrawals during retirement are tax-free, making Roth IRAs a popular choice for those who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement.
3. 401(k) Plans
401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement accounts that allow employees to contribute a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis. These contributions, along with any employer match, grow tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement, when they are subject to income tax.
4. Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs
SEP IRAs are retirement plans for self-employed individuals and small business owners. Contributions are made by the employer on a pre-tax basis and are tax-deductible. The earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal in retirement, when they are taxed as ordinary income.
5. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
While primarily designed for healthcare expenses, HSAs can also serve as retirement savings accounts. Contributions to HSAs are made with pre-tax dollars, and the earnings grow tax-free. Qualified withdrawals for medical expenses are also tax-free.
Understanding the benefits and features of these tax-advantaged retirement accounts is essential for effective retirement tax planning. By utilizing these accounts strategically, you can maximize your savings and minimize your tax liability in retirement.
Strategies to Minimize Taxes in Retirement
When it comes to planning for retirement, taxes play a crucial role in securing your financial future. Here are some effective strategies to consider to minimize taxes during retirement:
1. Contribute to Retirement Accounts
Maximize your contributions to tax-advantaged retirement accounts such as 401(k)s or Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). By doing so, you can take advantage of tax-deferred growth and potentially lower your taxable income.
2. Utilize Roth IRA
Consider converting a portion of your traditional IRA to a Roth IRA. While you’ll pay taxes on the conversion amount, future withdrawals from a Roth IRA are tax-free, providing tax diversification in retirement.
3. Manage Your Social Security Benefits
Be mindful of how Social Security benefits can impact your tax situation. Depending on your overall income, a portion of your benefits may be subject to taxation. Strategically managing other sources of income can help minimize the tax burden.
4. Prioritize Tax-Efficient Investments
Invest in tax-efficient funds or municipal bonds that generate tax-free income. These investments can help minimize your tax liability and maximize your after-tax returns.
5. Plan for Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Once you reach the age of 72, you’ll be required to take minimum distributions from your tax-deferred retirement accounts. Strategically planning these distributions can help optimize your tax situation.
6. Consider Charitable Giving
Explore the option of donating to charities as a way to reduce your taxable income. Charitable contributions can provide both financial benefits and the opportunity to make a positive impact.
By implementing these strategies and working with a financial advisor, you can develop a tax-efficient retirement plan that helps secure your financial future.
Long-term Tax Planning for a Secure Retirement
When it comes to planning for your retirement, tax considerations play a crucial role in ensuring a secure financial future. Effective tax planning can help maximize your savings and minimize tax obligations, allowing you to make the most of your retirement funds.
One essential aspect of long-term tax planning for retirement is understanding the different types of retirement accounts available to you. Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s offer tax-deferred growth, meaning you don’t pay taxes on contributions or investment gains until you withdraw the funds during retirement. On the other hand, Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s provide tax-free growth, allowing you to withdraw the funds tax-free during retirement.
Another strategy for tax planning in retirement is managing your income streams. By strategically withdrawing money from different retirement accounts, you may be able to optimize your tax liabilities. For instance, if you have both a traditional and a Roth account, withdrawing from the Roth account first can effectively minimize your taxable income and tax rate.
Diversifying your investments is also a key consideration for long-term tax planning. By having a mix of taxable and tax-advantaged accounts, such as municipal bonds or index funds, you can potentially achieve a more favorable tax situation. This diversification can provide flexibility in managing your tax exposure and give you options to minimize your tax burden in retirement.
Additionally, staying informed about changes in tax laws and regulations is vital to adapt your tax planning strategies. Tax laws can evolve over time, and keeping up with these changes ensures that you are taking advantage of any new opportunities or benefits.
In conclusion, long-term tax planning is essential for securing your retirement. By understanding different retirement accounts, managing income streams, diversifying investments, and staying informed about tax laws, you can ensure a financially stable and tax-efficient retirement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tax planning for retirement is a crucial step in securing your future financial stability. By strategically utilizing various retirement accounts, taking advantage of tax deductions and credits, and making informed decisions about when to withdraw funds, individuals can minimize their tax liabilities and maximize their savings. It is important to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to create a personalized tax plan that aligns with your retirement goals and objectives.