The role of central banks in the global economy is crucial and multi-faceted. As the guardians of monetary policy, they have the power to control interest rates, manage inflation, and ensure financial stability. Moreover, central banks play a pivotal role in fostering economic growth and managing crises, making their actions integral to the overall health and stability of the global economy.
Introduction to Central Banks and their Functions
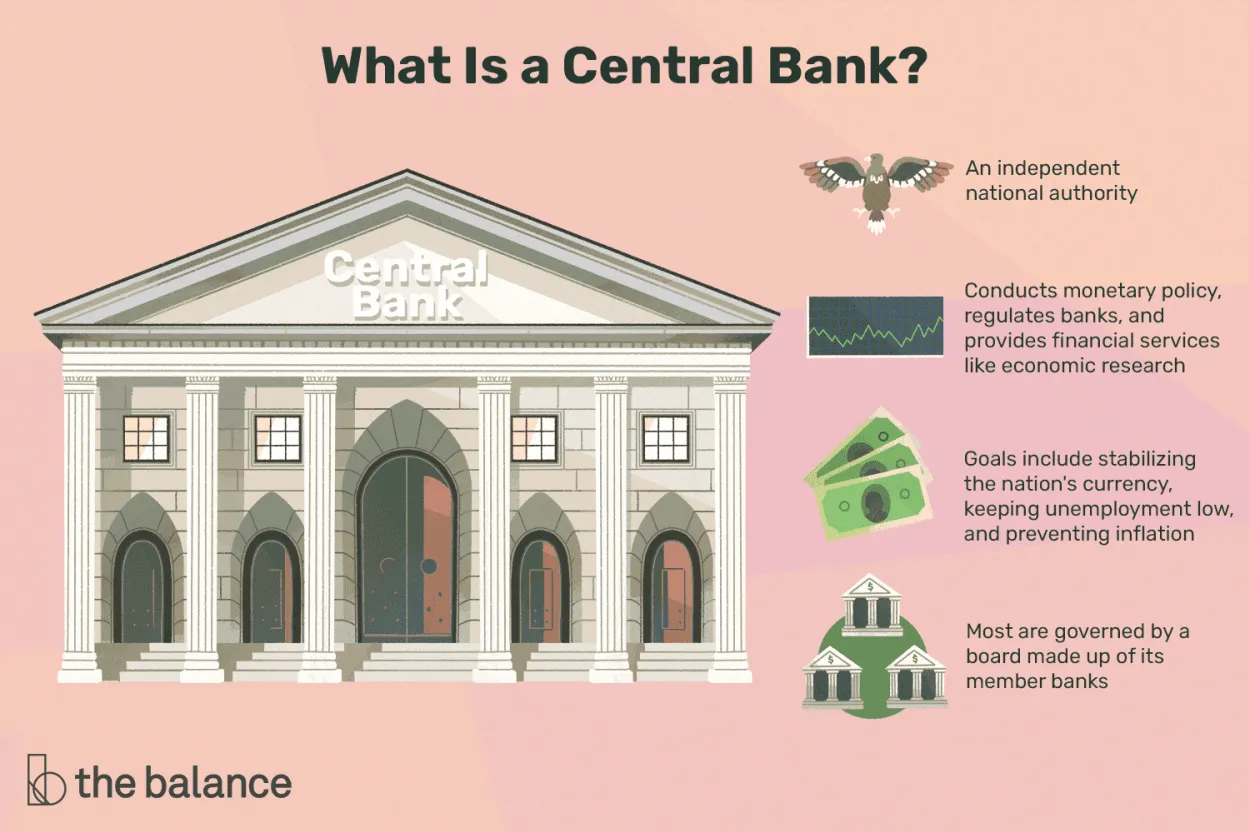
Central banks play a crucial role in the global economy, serving as the backbone of a country’s financial system. Their primary functions are to control monetary policy, maintain price stability, supervise the banking system, and act as lenders of last resort.
One of the main responsibilities of central banks is to control monetary policy. They do this by managing interest rates, adjusting reserve requirements, and conducting open market operations. These tools influence the money supply, which in turn affects borrowing costs, inflation, and economic growth.
Price stability is another key function of central banks. By keeping inflation in check, they promote economic stability and ensure that the value of a country’s currency remains relatively stable. This allows businesses and individuals to plan and make decisions with confidence.
In addition, central banks supervise the banking system to maintain its soundness and stability. They regulate banks, set guidelines for risk management, conduct stress tests, and monitor compliance with regulations. This oversight helps prevent financial crises and protects depositors’ funds.
Furthermore, central banks act as lenders of last resort. In times of financial distress, they provide liquidity to banks and financial institutions to prevent systemic disruptions. This function is crucial in maintaining confidence in the financial system and preventing panic among depositors and investors.
Overall, central banks play a vital role in ensuring the stability and smooth functioning of the global economy. Their functions extend beyond the national level, as they often collaborate and coordinate with other central banks to address global financial challenges and maintain monetary stability.
Monetary Policy and its Impact on Economy
The Role of Central Banks in Global Economy
Central banks play a crucial role in the global economy, and one of the key tools they use is monetary policy. Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by these banks to manage the money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions in a country or a group of countries. The objective of monetary policy is to achieve and maintain stability in prices, promote economic growth, and maintain employment levels.
One of the primary tools of monetary policy is the setting of interest rates. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence borrowing costs, which in turn affects consumer spending, borrowing, and investment decisions. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and stimulate economic activity, while higher rates restrict borrowing and help control inflation.
Another important tool of monetary policy is open market operations, which involve the buying and selling of government securities in the open market. When central banks buy government securities, they inject money into the economy, which increases the money supply and stimulates economic growth. Conversely, when they sell government securities, they decrease the money supply, which helps to control inflation.
Central banks also have the authority to regulate commercial banks and set reserve requirements. By adjusting reserve requirements, central banks can influence the amount of money that commercial banks are required to hold as reserves, thereby affecting the amount of money available for lending. This tool allows central banks to maintain control over money supply and credit conditions.
Overall, the monetary policy implemented by central banks has a profound impact on the economy. Changes in interest rates, open market operations, and reserve requirements can influence consumer spending, investment, inflation, and employment levels. Therefore, it is essential for central banks to carefully analyze economic indicators and make well-informed decisions to promote economic stability and growth.
How Central Banks Ensure Financial Stability
Central banks play a crucial role in maintaining financial stability in the global economy. Through various mechanisms, these institutions aim to create a safe and sound financial system that can withstand shocks and promote sustainable economic growth.
One of the key ways central banks ensure financial stability is through the regulation and supervision of financial institutions. They establish prudential norms and guidelines that banks and other financial entities must adhere to. By setting minimum capital requirements, conducting regular inspections, and enforcing regulations, central banks help prevent excessive risk-taking and limit the possibility of financial failures that can have widespread systemic effects.
In addition to regulation, central banks also act as lenders of last resort. During times of financial stress, they provide liquidity to troubled financial institutions when no one else is willing or able to do so. This helps stabilize the banking system and prevents panic withdrawals and bank runs that can lead to broader financial crises.
Central banks also implement monetary policy to maintain price stability and promote economic growth. By adjusting interest rates, controlling the money supply, and managing exchange rates, they influence borrowing costs, inflation levels, and economic activity. These actions help stabilize the overall economy and contribute to financial stability.
Furthermore, central banks engage in macroprudential policies to address systemic risks that may arise from excessive credit growth, asset price bubbles, or high levels of debt. They set limits on bank lending, monitor financial markets, and introduce measures to curb speculative behavior. By focusing on the overall health of the financial system, central banks can preemptively address vulnerabilities and reduce the likelihood of future crises.
In conclusion, central banks are pivotal in ensuring financial stability in the global economy. Their roles as regulators, lenders of last resort, managers of monetary policy, and promoters of macroprudential policies collectively contribute to a resilient and stable financial system. By maintaining financial stability, central banks play a crucial part in supporting sustainable economic growth and protecting the well-being of individuals and businesses worldwide.
The Role of Central Banks in Crisis Management
Central banks play a crucial role in managing and mitigating economic crises in the global economy. Their primary objective is to maintain price stability and ensure the smooth functioning of financial systems. However, in times of crisis, their responsibilities expand to include crisis management.
During a crisis, central banks employ different measures to stabilize economies and prevent further deterioration. One of the key tools is monetary policy, where central banks adjust interest rates and control the money supply. By reducing interest rates, central banks encourage borrowing and spending, which boosts economic activity.
In addition to monetary policy, central banks also act as lenders of last resort. They provide liquidity to financial institutions that are facing liquidity shortages, preventing bank runs and systemic collapses. This ensures the stability of the financial system and maintains confidence among investors and the public.
Central banks also play a vital role in maintaining financial market stability during crises. They may intervene by buying government bonds or other assets to inject liquidity into the markets. This helps stabilize prices and prevents panic selling, which can exacerbate the crisis.
Moreover, central banks act as regulators and supervisors, monitoring the health of financial institutions and implementing policies to strengthen their resilience to shocks. They impose stricter regulations and capital requirements to prevent excessive risk-taking and maintain the stability of the banking sector.
In conclusion, central banks have a multifaceted role in crisis management. From implementing monetary policy to providing liquidity, ensuring financial market stability, and regulating the financial sector, they play a crucial part in mitigating the impact of economic crises and maintaining the stability of the global economy.
Conclusion
The role of central banks in the global economy is undeniably significant. They play a crucial role in managing monetary policy, ensuring price stability, and promoting economic growth. Through their actions, central banks have the power to influence interest rates, regulate financial institutions, and provide liquidity during times of crisis. Their decisions have far-reaching impacts on global financial markets and can affect various sectors of the economy. Overall, central banks hold the responsibility of maintaining stability and fostering sustainable economic development worldwide.