Understanding Mutual Funds: An Investor’s Handbook is a comprehensive guide that offers insights into the world of mutual funds. This article aims to help investors gain a clear understanding of how mutual funds work and provides valuable information to make informed investment decisions.
An Introduction to Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are an investment option that allows individuals to pool their money together and invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
One of the key advantages of mutual funds is their diversification. By investing in a mutual fund, individuals can gain access to a wide range of securities, which helps to spread out the risk. This diversification can be particularly beneficial for investors who do not have the time or expertise to research and select individual investments.
Another benefit of mutual funds is their liquidity. Unlike other investment options such as real estate or fixed deposits, mutual funds can be bought or sold on any business day at the net asset value (NAV) price. This provides investors with the flexibility to enter or exit the market whenever they want.
Furthermore, mutual funds offer different types of funds to suit the investment goals and risk appetite of different individuals. For example, there are equity funds that invest predominantly in stocks, bond funds that invest in fixed-income securities, and balanced funds that invest in a mix of stocks and bonds.
When investing in mutual funds, it is important for investors to consider factors such as the fund’s historical performance, expense ratio, and the fund manager’s track record. These factors can have a significant impact on the returns generated by the mutual fund investment.
Determining Risk and Return
Understanding Mutual Funds: An Investor’s Handbook
When it comes to investing in mutual funds, one of the key factors to consider is the relationship between risk and return. Risk refers to the potential for loss or volatility in the value of an investment, while return represents the profit or gain an investment can generate.
Before investing in mutual funds, it is important for investors to determine their risk tolerance. This involves assessing how much risk they are willing and able to take on in pursuit of potential returns. Different mutual funds come with varying levels of risk, so investors need to carefully consider their financial goals and time horizon.
There are different types of mutual funds that offer potential returns based on their associated risks. Equity funds, for example, invest in stocks and tend to have higher potential returns but also higher volatility. Bond funds, on the other hand, invest in fixed-income securities and generally offer lower returns but are considered safer investments.
In addition to determining risk tolerance, investors should also thoroughly research and analyze a mutual fund’s performance history, expense ratio, and fund manager’s track record. This information can help investors gauge the potential risk and return of the fund.
It is essential for investors to remember that risk and return are interconnected. Higher potential returns often come with higher risks, while lower risks tend to offer lower returns. Therefore, finding the right balance between risk and return is crucial in building a well-diversified investment portfolio.
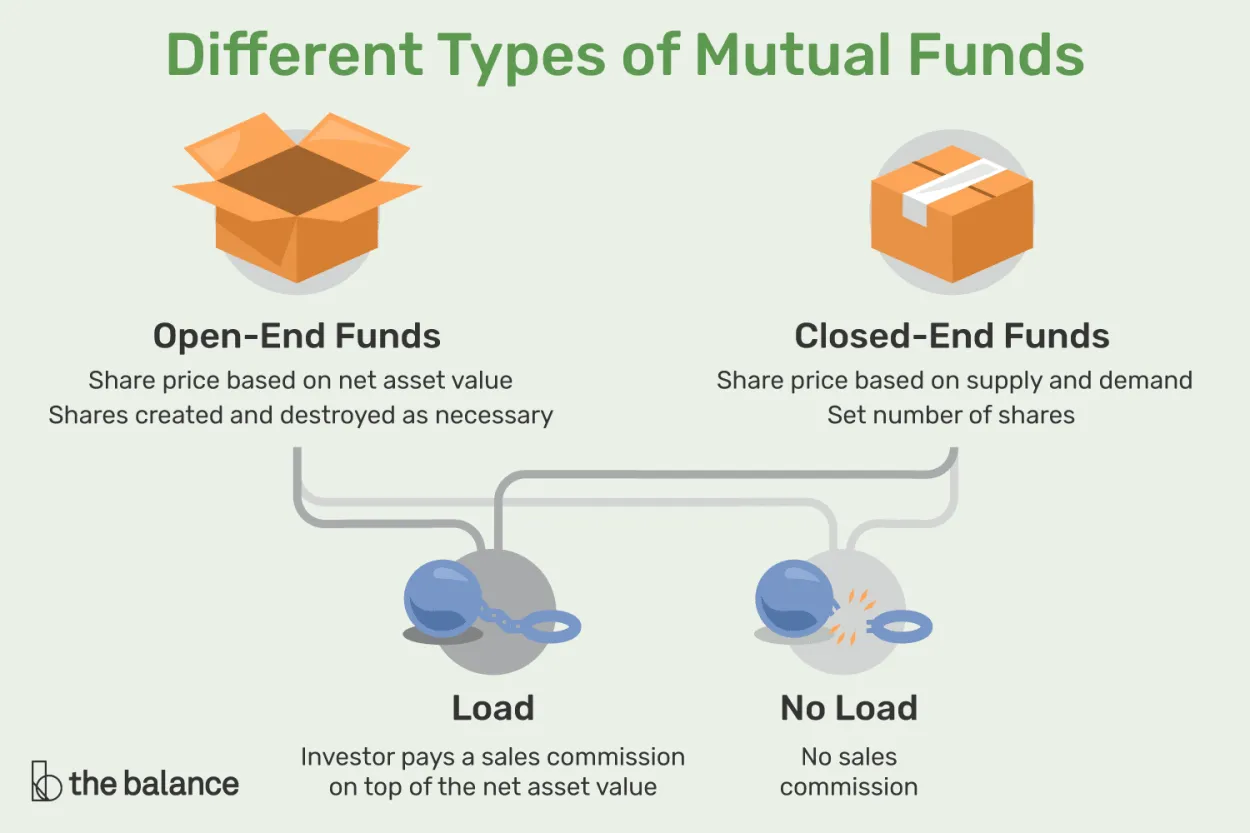
Types of Mutual Funds
When it comes to investing in mutual funds, it’s important to understand that there are various types available. Each type has its own characteristics and investment goals, catering to different investor needs and risk appetites. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of mutual funds:
1. Equity Funds
Equity funds, also known as stock funds, primarily invest in stocks. These funds aim to generate long-term capital appreciation by investing in companies with growth potential. Equity funds can focus on specific sectors, market capitalizations, or regions.
2. Bond Funds
Bond funds, also called fixed-income funds, invest in fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, and other debt instruments. These funds aim to provide a regular income stream while preserving capital.
3. Money Market Funds
Money market funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities such as Treasury bills, certificates of deposit, and commercial paper. These funds are suitable for investors looking for stability and liquidity.
4. Balanced Funds
As the name suggests, balanced funds invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. These funds aim to achieve both capital appreciation and income generation, providing investors with a balanced investment approach.
5. Index Funds
Index funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These funds aim to replicate the performance of the index they track, offering investors a low-cost investment option.
6. Sector Funds
Sector funds focus on specific industries, such as technology, healthcare, or energy. These funds provide investors with the opportunity to concentrate their investments in particular sectors they believe will perform well.
7. International Funds
International funds invest in securities outside the investor’s home country. These funds provide exposure to global markets and allow investors to diversify their portfolios geographically.
Understanding the different types of mutual funds is essential for investors to align their investment goals and risk tolerance with the most suitable fund. It’s important to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.
Choosing the Right Fund for You
When it comes to investing in mutual funds, it’s important to understand that not all funds are created equal. Each fund has its own investment strategy, risk level, and potential returns. Therefore, choosing the right fund that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance is crucial. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a mutual fund:
1. Investment Objectives
First and foremost, evaluate your investment objectives. Are you looking for long-term growth, income generation, or capital preservation? Different funds are designed to meet different objectives, so you should choose one that matches your financial goals.
2. Risk Appetite
Assess your risk appetite. Mutual funds can range from low-risk bond funds to high-risk equity funds. Generally, higher returns come with greater volatility. If you have a higher risk tolerance and a longer investment horizon, you may consider investing in equity funds. However, if you prefer stability and are risk-averse, bond funds or money market funds might be more suitable.
3. Diversification
Consider the diversification offered by the fund. Diversifying your investments across different asset classes and sectors can help reduce the overall risk in your portfolio. Look for funds that provide a mix of stocks, bonds, and possibly other assets.
4. Track Record
Examine the fund’s track record and performance over time. While past performance does not guarantee future results, it can give you insights into the fund manager’s expertise and consistency. Look for funds that have consistently outperformed their benchmarks and peers.
5. Expenses
Compare the costs associated with the fund. Mutual funds charge various fees, including management fees, administrative expenses, and loads (sales charges). Lower expenses can have a significant impact on your overall returns, so it’s important to select funds with reasonable costs.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right mutual fund for your investment needs. Remember, always conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor if needed.
Conclusion
Understanding mutual funds is essential for investors looking to grow their wealth. These investment vehicles offer diversification, professional management, and easy accessibility. By conducting thorough research, individuals can choose mutual funds that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance. With the potential for long-term returns, mutual funds provide a viable option for both novice and experienced investors.