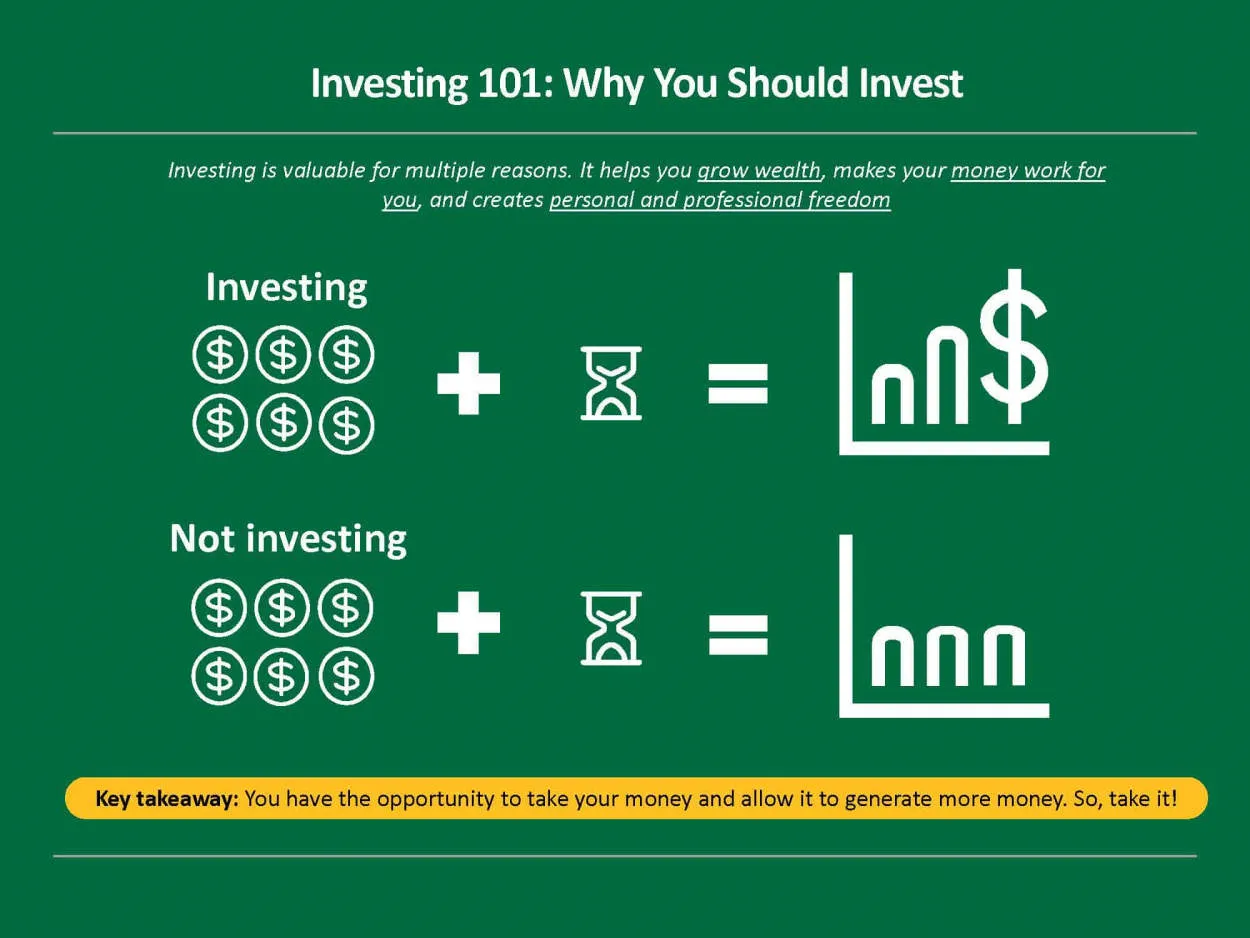
Are you eager to gain financial independence and secure your future? Look no further! In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of investing, equipping you with the knowledge and tools needed for personal financial growth. From understanding different investment options to managing risk, join us as we navigate the world of investing and unlock the keys to a prosperous future.
The Importance of Investing for Personal Financial Growth
Investing is a crucial aspect of personal financial growth. It refers to the process of allocating money or resources with the expectation of generating a profitable return in the future. While some may view investing as a complex and risky endeavor, it is imperative to understand the benefits it can bring to one’s financial well-being.
First and foremost, investing enables individuals to grow their wealth and achieve their financial goals. By putting money into various investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, individuals have the potential to earn significant returns over time. This growth can provide financial security, ensure a comfortable retirement, or even offer opportunities for personal fulfillment and experiences.
Furthermore, investing allows individuals to keep pace with inflation. Inflation is the gradual increase in prices over time, leading to the erosion of purchasing power. By investing, individuals can generate returns that outpace inflation, ensuring that their money retains its value and can afford them a better standard of living in the future.
Investing also offers the potential for passive income. Certain investments, such as dividend-paying stocks or rental properties, can provide individuals with regular income without requiring active participation. This additional income stream can provide financial stability and open doors to pursue new opportunities or achieve long-held aspirations.
Lastly, investing cultivates financial discipline and educated decision-making. It requires individuals to conduct research, analyze risks and potential rewards, and make informed choices. By engaging in investing, individuals can gain valuable knowledge about financial markets, economic trends, and various industries, enabling them to make better financial decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
In conclusion, investing is a vital tool for personal financial growth. It allows individuals to grow their wealth, combat inflation, generate passive income, and develop financial acumen. However, it is crucial to approach investing with careful consideration and seek professional advice when necessary. With diligence, patience, and an understanding of investing fundamentals, individuals can unlock the potential for long-term financial success.
Understanding Different Asset Classes: Stocks, Bonds, and Mutual Funds
When it comes to investing, there are various asset classes that individuals can consider. In this article, we will focus on three main asset classes: stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Stocks: Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder and have the potential to earn profits through dividends and capital gains. However, prices can be volatile and affected by market fluctuations.
Bonds: Bonds are fixed-income securities issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. When you invest in bonds, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments over a specified period of time. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks but may offer lower returns.
Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in various securities, such as stocks, bonds, or a combination of both. They are managed by professional fund managers who aim to achieve specific investment objectives. Mutual funds provide diversification and are suitable for those who prefer a hands-off approach to investing.
Each asset class has its own characteristics, risk levels, and potential returns. The decision to invest in stocks, bonds, or mutual funds depends on factors such as individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. It is important to thoroughly research and understand each asset class before making any investment decisions.
Crafting a Personal Investment Plan: Setting Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
When it comes to personal financial growth, having a well-designed investment plan is crucial. To start off on the right foot, it’s important to set clear financial goals and assess your risk tolerance.
Setting Financial Goals
The first step in crafting a personal investment plan is to establish your financial goals. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Consider short-term goals, such as saving for a down payment on a house, as well as long-term goals, such as retirement savings.
By defining your financial goals, you gain clarity on what you want to achieve and can create an investment strategy tailored to your needs. Remember to set realistic expectations and be flexible as your goals may change over time.
Evaluating Risk Tolerance
Understanding your risk tolerance is equally important in creating a personal investment plan. Risk tolerance refers to your comfort level with the possibility of losing money in pursuit of higher returns. It varies from individual to individual based on factors such as age, financial stability, and investment knowledge.
To evaluate your risk tolerance, consider your investment time horizon, financial obligations, and emotional capacity to handle market fluctuations. Are you willing to take on more risk for potentially higher returns or do you prefer a more conservative approach?
Once you have a clear understanding of your risk tolerance, you can align your investment decisions accordingly. This may involve diversifying your portfolio, adjusting asset allocations, or seeking professional advice.
In Conclusion
Investing 101: Basics for Personal Financial Growth starts with crafting a personal investment plan that revolves around your financial goals and risk tolerance. By setting clear objectives and understanding your comfort level with risk, you can create a roadmap for long-term financial success. However, keep in mind that investing is a continuous process that requires regular review and adjustment to stay on track towards your goals.
Investment Strategies for Different Life Stages: Young Professionals, Families, and Retirees
When it comes to investing, it’s important to tailor your strategies based on your life stage. Different life stages present varying financial goals, time horizons, and risk tolerance levels. In this article, we will explore investment strategies for young professionals, families, and retirees.
Young Professionals
For young professionals just starting their careers, it’s crucial to focus on long-term investment growth. With time on their side, young professionals can take on more risk in exchange for higher returns. Here are some key investment strategies:
- Diversify your portfolio by investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
- Consider investing in individual stocks of promising companies or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Take advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s and contribute enough to receive the maximum employer match.
- Keep learning about personal finance and investments to make informed decisions.
Families
For families, the focus shifts towards balancing growth and stability. Important considerations include saving for education expenses and ensuring financial security. Here are some investment strategies for families:
- Allocate a portion of your investment portfolio towards low-risk investments like bonds or money market funds.
- Invest in tax-advantaged college savings plans, such as 529 plans, to fund your children’s education.
- Create an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Consider investing in real estate as a long-term investment option.
Retirees
Retirees typically have a lower risk tolerance and prioritize generating income from their investments. The focus is on preserving wealth and maintaining a steady cash flow. Here are some investment strategies for retirees:
- Shift a portion of your portfolio towards more conservative investments, such as bonds or dividend-paying stocks.
- Consider annuities or other guaranteed income products to ensure a stable income stream.
- Take advantage of catch-up contributions to retirement accounts if eligible.
- Regularly assess your investment portfolio and make adjustments based on changing financial needs.
Conclusion
Investing is a crucial aspect of personal financial growth. By understanding the basics mentioned in this article, individuals can develop a solid foundation for making informed investment decisions. It is important to remember that investing involves risk, but with proper research and careful planning, anyone can embark on a journey towards financial prosperity.